Let’s take a quick trip back in time before Edge Computing. In the early days of the internet, we waited — sometimes painfully — for web pages to load, videos to buffer, or downloads to complete. That’s because almost everything had to travel across long distances to massive centralised data centres before it could show up on your screen.
Fast forward to 2025, and the conversation is no longer just about cloud computing. It’s about edge computing — the idea that your devices, from your smartphone to your smart fridge to your industrial robot, shouldn’t have to send data halfway across the world to get things done.
Instead, the edge — the local device, the nearby router, the city-based micro data center — is becoming the new frontier of computing. And if you’re wondering whether this is just another tech buzzword, it’s not. Edge computing is real, it’s here, and it’s reshaping everything from how we drive to how we heal.
Let’s unpack what it means, where it’s being used, and how it could quietly become one of the biggest tech shifts of the decade.
🧠 What Is Edge Computing, Really?
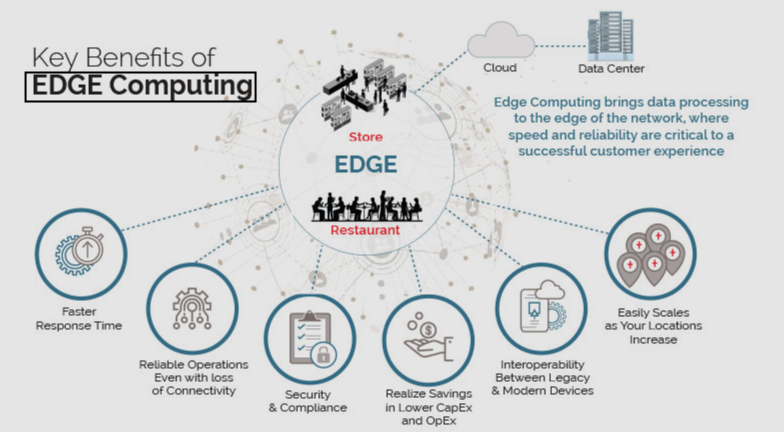
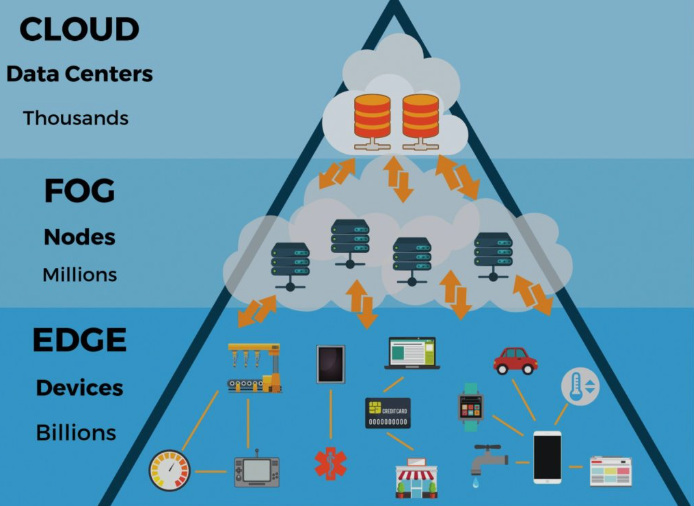
At its core, edge computing means processing data closer to where it’s created instead of sending it off to centralized cloud servers. The “edge” refers to the literal edge of the network — think devices like your smartphone, smart speaker, security camera, or factory sensor.
Instead of constantly pinging a distant cloud server, these devices can analyze, filter, and act on data locally, only sending what’s necessary to the cloud. The benefits? Less latency, better performance, enhanced privacy, and reduced bandwidth usage.
In a world where milliseconds matter — like autonomous driving or remote surgery — edge computing isn’t just helpful. It’s essential.
read this related article which gives you new insight of cloud computing as Saas
🌍 Why Edge Computing Is Booming in 2025
There’s a reason this concept is exploding right now. It’s not just hype — it’s necessity.
Here’s what’s driving the edge revolution:
1. The IoT Explosion
We now have 15+ billion connected devices globally — from smart toasters to industrial robots. These devices produce enormous amounts of data, and it’s not practical or efficient to send all of that to the cloud.
2. 5G and Ultra-Fast Networks
With 5G now widely deployed in many parts of the world, devices can communicate faster. But to take full advantage of that speed, you need nearby processing — which is exactly what edge computing delivers.
3. AI at the Edge Computing
Modern edge devices are powerful enough to run AI algorithms locally. That means smarter decisions — like detecting faces, analyzing traffic, or flagging security threats — can happen instantly without relying on a cloud roundtrip.
4. Data Privacy Regulations
Laws like GDPR and India’s DPDP Act are making it harder to move sensitive data freely across borders. Keeping data local via edge computing can help companies stay compliant.
Real-Life Applications: Edge Computing in Action
Let’s step away from theory and get practical. Where is edge computing actually being used today? A lot more places than you might think.
🚗 1. Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars are perhaps the ultimate edge devices. They generate gigabytes of data per second from cameras, LiDAR, and sensors — and they need to react in real time. There’s no time to wait for cloud instructions when a child runs into the street.
Edge benefit: Instant decision-making for navigation, obstacle detection, and safety.
🏥 2. Healthcare Monitoring
Wearables and medical devices can now monitor vitals like heart rate, oxygen saturation, and glucose levels in real-time — and alert doctors or family members if something’s wrong.
Edge benefit: Faster intervention, reduced need for constant connectivity, and enhanced privacy.
🏭 3. Smart Manufacturing
Edge computing is transforming factories into smart factories, where machines can self-monitor, detect maintenance needs, and adjust operations automatically.
Edge benefit: Reduced downtime, better efficiency, and predictive maintenance.
🛍️ 4. Retail
Retailers are using edge AI for real-time video analytics, inventory tracking, and even personalized customer experiences as shoppers walk through stores.
Edge benefit: Real-time insights, reduced lag, and better customer engagement.
📹 5. Smart Cities
From traffic monitoring to public safety to waste management, cities are deploying edge sensors to process data locally.
Edge benefit: Faster response times, local decision-making, and less reliance on centralized infrastructure.
⚙️ Under the Hood: How Edge Computing Works
Here’s a simple analogy: Imagine cloud computing is like a huge supermarket on the outskirts of town. Edge computing is like a local corner store — smaller, closer, and faster for everyday needs.
Edge devices contain mini processors and sometimes even dedicated AI chips. They can run models, filter raw data, and only send meaningful results to the cloud. For example:
- A smart security camera can identify motion and distinguish between a dog, a person, or a tree branch — and only alert you when it matters.
- A thermostat can learn your habits and adjust heating locally without needing cloud input.
The core technologies powering this include:
- Edge servers or micro data centers
- AI inference chips (e.g., NVIDIA Jetson, Google Coral)
- 5G networks
- Containerization and Kubernetes at the edge
- Custom edge platforms like AWS Greengrass, Azure IoT Edge, and Google Edge TPU
📉 Challenges Holding Edge Back (for Now)
Like any powerful technology, edge computing isn’t perfect. Here are some real-world hurdles:
🔋 1. Power and Hardware Constraints
Edge devices often have limited power, storage, and compute capabilities. Running complex AI models on them can be tricky — though this is improving fast.
🧩 2. Fragmentation
There’s no universal standard for edge systems yet. Every device, manufacturer, and platform may use different architectures and software.
🔒 3. Security Risks
While edge computing can enhance privacy by keeping data local, it also increases the attack surface. Each edge node becomes a potential vulnerability.
💰 4. Deployment Costs
Setting up edge infrastructure, especially in remote or large-scale environments, can be expensive up front — though costs are falling rapidly.
📈 Market Trends and Future Outlook
The edge computing market is booming. According to Statista, global spending on edge computing is projected to hit $317 billion by 2026, up from $176 billion in 2022. Industries leading the charge include:
- Manufacturing
- Healthcare
- Telecommunications
- Retail
- Energy and utilities
By 2030, analysts predict over 75% of enterprise-generated data will be processed at the edge.
🧭 What This Means for You (Even If You’re Not a Tech Giant)
Edge computing isn’t just for big corporations. It’s quietly becoming part of daily life:
- Your smart speaker that responds instantly? That’s edge AI.
- Your phone unlocking with your face — without internet? Edge AI again.
- Your doorbell recognizing visitors before you check the app? Edge, edge, edge.
As more apps and devices become edge-enabled, users will notice:
- Faster performance
- Less lag
- Smarter personalization
- Greater privacy control
And for developers, startups, and businesses — edge represents a huge opportunity to create faster, safer, more responsive solutions.
🔮 What’s Coming Next in Edge Computing?
Expect to see these trends over the next 2–3 years:
🧠 1. Smarter Edge AI
We’ll see more devices that run transformer-based models like ChatGPT or Gemini, but locally. Imagine having real-time language models on your phone or car — with no internet needed.
🧳 2. Edge + Cloud Hybrid Models
The best systems will use a hybrid model, doing fast local processing and sending deeper tasks to the cloud for long-term analysis.
🛰️ 3. Edge Computing in Remote Areas
Edge computing will help bring digital services to rural and remote areas where cloud connectivity is limited — think agriculture, mining, and conservation.
🧬 4. Personalized Health at Home
Expect more FDA-approved edge-based medical tools: real-time diagnostics, AI-driven ECGs, and even predictive care alerts powered by local AI.
🧩 Final Thoughts: Is Edge Computing the New Cloud computing?
Let’s be clear — edge computing doesn’t replace the cloud. It complements it.
But the balance is shifting.
Where cloud once dominated everything, edge computing is carving out its role in places where speed, privacy, and real-time performance matter most.
It’s not flashy like VR or as hyped as general AI — but it’s arguably more important. Because the more we rely on connected devices, the more we’ll need them to think for themselves.
So whether you’re a business leader, a developer, or just someone who wants their smart home to feel a bit smarter — edge computing is no longer the future. It’s already at your doorstep.

